Engineering Data
Selection
Choosing A Rope
Always consult the manufacturer before using rope when personal safety or possible damage to property is involved.
Make sure the rope is adequate for the job. Do not use too small a rope or the wrong type.
| Product | Strength Scale 1-5 (5 = strongest, diameter to diameter) |
Elastic Elongation at Working Load % | Weight Scale 1-5 (5 = heaviest, diameter to diameter) |
Working Energy Absorption Ft Lbs/Lb of Rope |
Maximum Energy Absorption Ft Lbs/Lb of Rope |
Rope Average Specific Gravity g/cc |
Splice Complexity Scale 1-5 (5 = most complex) |
Dielectric Leakage, New/Dry, at 100 kV AC, 2ft. Spacing, in Micro-Amperes*** (250 Max allowable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aracom Miniline | 2.9 | 0.6 | 4.0 | 100 | 4,906 | 1.40 | 5 | NA |
| Aracom T | 3.1 | 0.7 | 4.4 | 157 | 4,409 | 1.40 | 3 | NA |
| Aracom 100 | 3.8 | 0.9 | 3.9 | 426 | 8,144 | 1.44 | 1 | <250 |
| Crystalyne | 2.7 | 0.5 | 4.3 | 187 | 3,403 | 1.40 | 3 | <100 |
| Double Esterlon | 1.4 | 2.2 | 3.9 | 291 | 7,711 | 1.38 | 2 | <20 |
| Hy-Dee Brait | 0.7 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 116 | 12,673 | 0.93 | 3* | <10 |
| Maxibraid | 3.5 | 0.7 | 3.3 | 226 | 6,342 | 0.97 | 1 | <100 |
| Maxibraid Plus | 2.7 | 0.6 | 3.7 | 115 | 4,295 | 1.18 | 3 | <100 |
| Mega Max | 2.9 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 318 | 8,300 | 0.97 | 3 | <100 |
| Nylon Brait | 1.3 | 10.0 | 2.9 | 1,426 | 23,680 | 1.14 | 3 | NA |
| Polydyne | 1.5 | 5.1 | 3.8 | 576 | 11,187 | 1.24 | 2 | >500 |
| PolyPlus Braid | 1.1 | 3.4 | 3.1 | 395 | 8,228 | 1.25 | 1 | <100 |
| Portland Braid | 1.3 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 265 | 5,929 | 1.38 | 2 | <20 |
| Ultrex | 5.0 | 0.6 | 3.1 | 318 | 8,300 | 0.97 | 1 | <100 |
| Unitrex XS 8 | 3.5 | 0.5 | 4.6 | NA | NA | 1.10 | 4 | <50 |
| Vectrus | 4.3 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 232 | 4,446 | 1.40 | 1 | <100 |
| Yalex | 1.7 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 409 | 10,700 | 1.38 | 1 | <100 |
| Yalon | 1.1 | 7.0 | 3.5 | 796 | 11,871 | 1.14 | 2 | >2000 |
| * Quick splice method available which reduces the break strength but also reduces the splice complexity to 1 ** NA in Dielectric leakage indicates that the product is not recommended for use in dielctric situations due to the ropes potential moisture gain ***Absorbed or entrained moisture or impurities will increase a ropes conductivity dramatically |
||||||||
Fiber Comparison Data
| Product | Strength Scale 1-5 |
Tenacity g/d |
Specific Gravity g/cc |
Weight Scale 1-5 |
Average Water Absorption % @65% RH |
Melting Point °F (©) |
Elastic Elongation Scale1-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon (NY) | 1.5 | 9.2 | 1.14 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 460 (240) | 5 |
| Polyester (PET) | 1.4 | 9.2 | 1.38 | 4.3 | 0.4 | 480 (255) | 3 |
| Polypropylene (PP), Polyethylene (PE) | 1.0 | 6.5 | 0.93 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 330 (165) | 4 |
| Co-Polymer (PP/PE) | 1.1 | 7.5 | 0.93 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 330 (165) | 3 |
| HMPE* (Spectra™, Dyneema™) | 4.8 | 36.0 | 0.97 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 300 (150) | 1 |
| Aramid (Technora, Twaron, Kevlar) | 3.8 | 28.0 | 1.44 | 4.8 | 4.0 | **900 (500) | 2 |
| Vectran (LCP) | 3.9 | 28.0 | 1.40 | 4.4 | 0.0 | 625 (330) | 1 |
| Zylon PBO | 5.0 | 45.0 | 1.56 | 5.0 | 1.3 | ***1200 (650) | 1 |
| * High Modulus Polyethylene ** Chars *** Decomposition temperature For computing energy-absorption requirements, refer to example in “Dynamic Loading.” For computing weight in sea water: (Wt. in Air) – (Wt. in Air)(1.03) / (Specific Gravity of Rope) |
|||||||
Components of Elongation
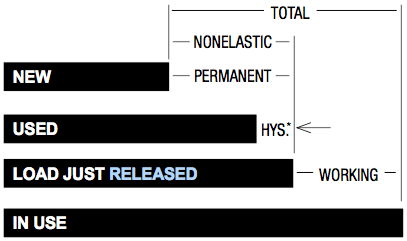
* Hysteresis refers to a recoverable portion of stretch over a period of time after a load is released.



